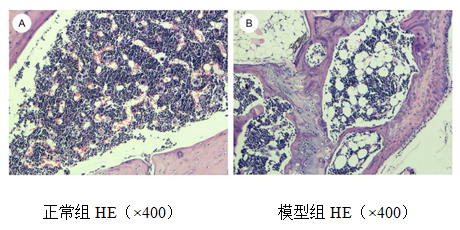
A rat model of aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia (AA) refers to anemia characterized by decreased bone marrow proliferation, accompanied by a decrease in whole blood cells caused by exposure to drugs, toxins, viruses, or unknown causes. China belongs to an area with a high incidence of AA, and children are in the age group with a high incidence of relapse. In order to explore the pathogenesis of AA and screen for effective prevention and treatment drugs, it is particularly important to establish a suitable animal model of AA. About half of AA is caused by contact with drugs or chemical factors, such as chemotherapy drugs, industrial pollution, heavy metal poisoning, etc. Now, a rat model of AA is established using the combination of 5-fluorouracil and Baixiaoan.
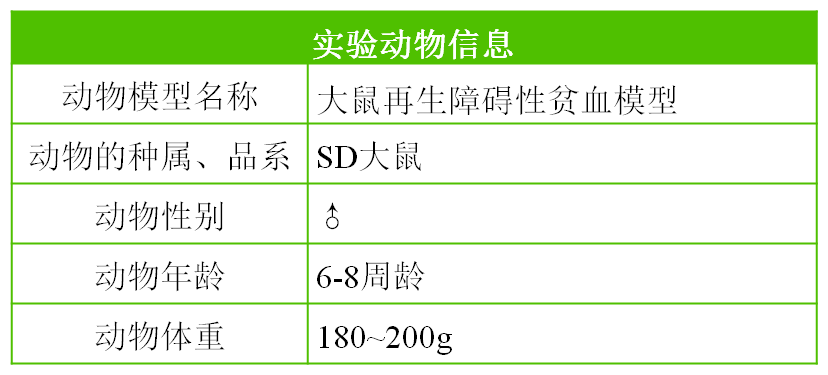
Observation indicators
Blood routine indicators such as peripheral white blood cells (WBC), platelets (PLT), red blood cells (RBC), and reticulocytes (Rtc) decrease. Bone marrow examination shows reduced proliferation of nucleated cells in the bone marrow, rare occurrence of megakaryocytes, and increased fat vacuoles.
Partial results display