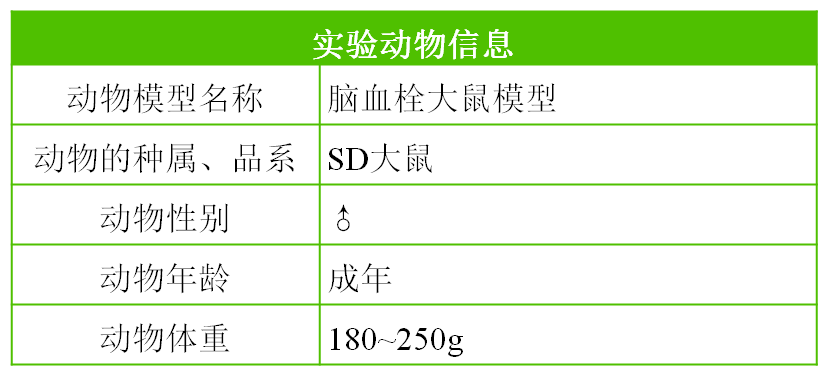
A rat model of cerebral thrombosis
Stroke, commonly known as stroke, includes cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral thrombosis, and cerebral infarction. Among them, cerebral thrombosis accounts for half of all stroke patients and is a common disease among middle-aged and elderly people. The disability rate of this disease is relatively high, and the quality of life of patients has significantly decreased. Therefore, research on the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral thrombosis is crucial. In order to better study the pathogenesis, pathological and physiological changes, and the efficacy of thrombolytic therapy of cerebral thrombosis, it is of great significance to establish an animal model of cerebral thrombosis that is similar to the pathogenesis of human and conforms to the thromboembolic nature of human blood. Compared with other experimental animals, rats are widely used as research objects for cerebral thrombosis due to their low cost, small variations in cerebral vascular anatomy, close proximity to human anatomy and physiology, long survival time of animals, and ability to conduct research on the pathological process of cerebral ischemia. The location of vascular damage is constant, and they are widely used as research objects for cerebral thrombosis
Observation indicators
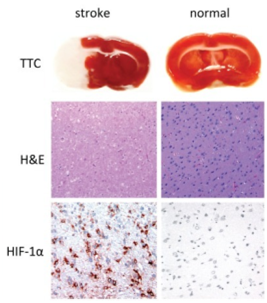
According to the Bederson score after animal awakening; Observe the infarct site with TTC staining; HE staining was used to observe the pathology of brain tissue; Immunohistochemical detection of hypoxia factor HIF-1 α expression; ELISA method was used to detect thromboxane B2 (TXB2) and 6-keto prostaglandin F1 alpha (6-keto-PGF1 alpha) in plasma; Intracranial micro CT scan or MRI scan.
Partial Results Display