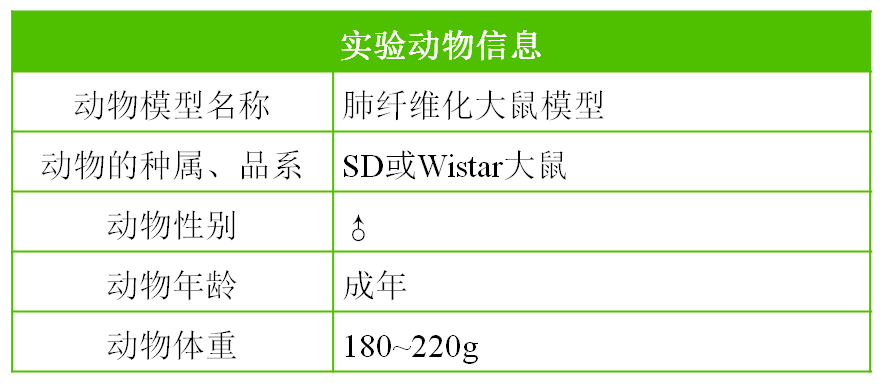
Pulmonary fibrosis rat model
The pathological characteristics of pulmonary fibrosis are repeated and persistent damage to alveoli caused by pulmonary inflammation, as well as the destruction, repair, and excessive deposition of extracellular matrix. This disease seriously affects the quality of life of patients and has a very poor prognosis. Due to the unclear pathogenesis of this disease and the lack of corresponding effective treatment methods in clinical practice, the mortality rate of patients remains high. Therefore, establishing a reliable and stable animal model of pulmonary fibrosis is an important prerequisite for exploring its pathogenesis and developing effective therapeutic drugs. The commonly used pulmonary fibrosis inducers in experiments include bleomycin, paraquat, silica, asbestos, radiation, reovirus, wild lily alkaloids, etc. Among these inducers, bleomycin is the most widely used and has become a classic inducer of animal pulmonary fibrosis models.
Observation indicators
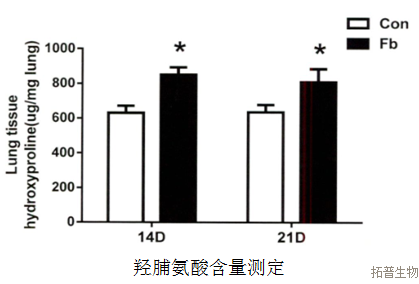
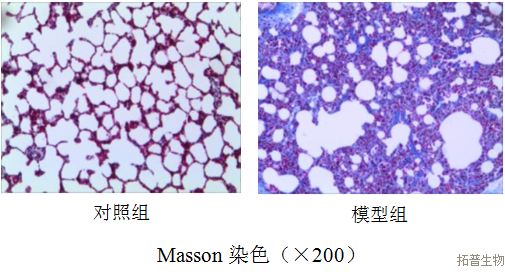
Inflammatory cell count, hydroxyproline, and pathological examination of lung tissue in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
Partial Results Display