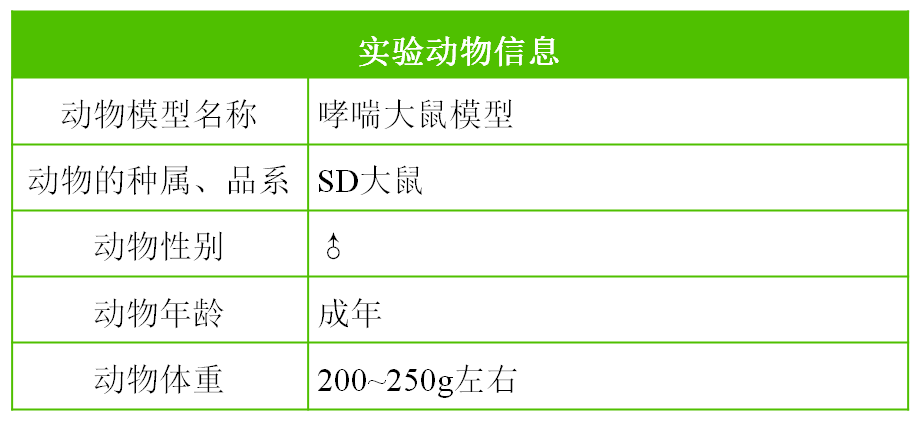
Asthma rat model
Bronchial asthma, abbreviated as asthma, is a disease characterized by airway allergic inflammation and airway responsiveness, with eosinophil and mast cell responses as the main features. Due to the complex pathogenesis of asthma, the etiology and pathogenesis are still unclear, and clinical trials are limited by ethics and methods. Therefore, it is necessary to construct an asthma animal model to study the occurrence and development of the disease and formulate corresponding treatment measures. Ovalbumin (OVA), also known as chicken egg white albumin, is the most commonly used allergen. The establishment of an asthma model in animals induced by OVA is a simple and easy method with strong operability and a high success rate.
Observation indicators
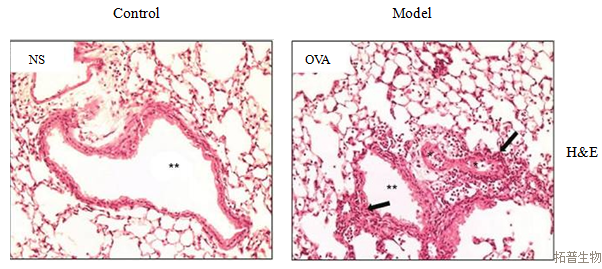
Total number of cells and EOS count in BALF; The pathological manifestations of lung tissue include damage to the alveolar wall structure, infiltration of inflammatory cells such as eosinophils and lymphocytes, and hypertrophy and proliferation of goblet cells in the airway.
Partial Results Display